Spring Cloud(十二):分布式链路跟踪 Sleuth 与 Zipkin【Finchley版】
随着业务发展,系统拆分导致系统调用链路愈发复杂一个前端请求可能最终需要调用很多次后端服务才能完成,当整个请求变慢或不可用时,我们是无法得知该请求是由某个或某些后端服务引起的,这时就需要解决如何快读定位服务故障点,以对症下药。于是就有了分布式系统调用跟踪的诞生。
现今业界分布式服务跟踪的理论基础主要来自于 Google 的一篇论文《Dapper, a Large-Scale Distributed Systems Tracing Infrastructure》,使用最为广泛的开源实现是 Twitter 的 Zipkin,为了实现平台无关、厂商无关的分布式服务跟踪,CNCF 发布了布式服务跟踪标准 Open Tracing。国内,淘宝的 “鹰眼”、京东的 “Hydra”、大众点评的 “CAT”、新浪的 “Watchman”、唯品会的 “Microscope”、窝窝网的 “Tracing” 都是这样的系统。
Spring Cloud Sleuth 也为我们提供了一套完整的解决方案。在本章中,我们将详细介绍如何使用 Spring Cloud Sleuth + Zipkin 来为我们的微服务架构增加分布式服务跟踪的能力。
Spring Cloud Sleuth
一般的,一个分布式服务跟踪系统主要由三部分构成:
- 数据收集
- 数据存储
- 数据展示
根据系统大小不同,每一部分的结构又有一定变化。譬如,对于大规模分布式系统,数据存储可分为实时数据和全量数据两部分,实时数据用于故障排查(Trouble Shooting),全量数据用于系统优化;数据收集除了支持平台无关和开发语言无关系统的数据收集,还包括异步数据收集(需要跟踪队列中的消息,保证调用的连贯性),以及确保更小的侵入性;数据展示又涉及到数据挖掘和分析。虽然每一部分都可能变得很复杂,但基本原理都类似。
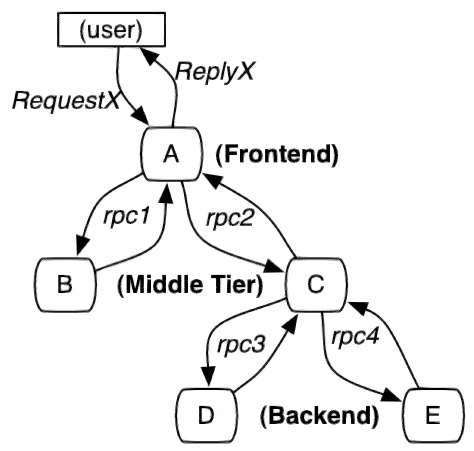
服务追踪的追踪单元是从客户发起请求(request)抵达被追踪系统的边界开始,到被追踪系统向客户返回响应(response)为止的过程,称为一个trace。每个 trace 中会调用若干个服务,为了记录调用了哪些服务,以及每次调用的消耗时间等信息,在每次调用服务时,埋入一个调用记录,称为一个span。这样,若干个有序的 span 就组成了一个 trace。在系统向外界提供服务的过程中,会不断地有请求和响应发生,也就会不断生成 trace,把这些带有 span 的 trace 记录下来,就可以描绘出一幅系统的服务拓扑图。附带上 span 中的响应时间,以及请求成功与否等信息,就可以在发生问题的时候,找到异常的服务;根据历史数据,还可以从系统整体层面分析出哪里性能差,定位性能优化的目标。
Spring Cloud Sleuth 为服务之间调用提供链路追踪。通过 Sleuth 可以很清楚的了解到一个服务请求经过了哪些服务,每个服务处理花费了多长。从而让我们可以很方便的理清各微服务间的调用关系。此外 Sleuth 可以帮助我们:
- 耗时分析: 通过 Sleuth 可以很方便的了解到每个采样请求的耗时,从而分析出哪些服务调用比较耗时;
- 可视化错误: 对于程序未捕捉的异常,可以通过集成 Zipkin 服务界面上看到;
- 链路优化: 对于调用比较频繁的服务,可以针对这些服务实施一些优化措施。
Spring Cloud Sleuth 可以结合 Zipkin,将信息发送到 Zipkin,利用 Zipkin 的存储来存储信息,利用 Zipkin UI 来展示数据。
这是 Spring Cloud Sleuth 的概念图: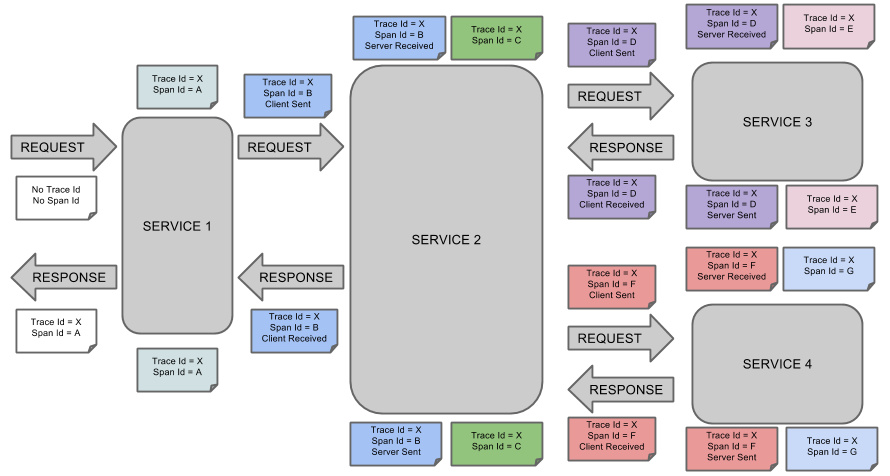
Zipkin
Zipkin 是 Twitter 的一个开源项目,它基于 Google Dapper 实现,它致力于收集服务的定时数据,以解决微服务架构中的延迟问题,包括数据的收集、存储、查找和展现。
我们可以使用它来收集各个服务器上请求链路的跟踪数据,并通过它提供的 REST API 接口来辅助我们查询跟踪数据以实现对分布式系统的监控程序,从而及时地发现系统中出现的延迟升高问题并找出系统性能瓶颈的根源。除了面向开发的 API 接口之外,它也提供了方便的 UI 组件来帮助我们直观的搜索跟踪信息和分析请求链路明细,比如:可以查询某段时间内各用户请求的处理时间等。
Zipkin 提供了可插拔数据存储方式:In-Memory、MySql、Cassandra 以及 Elasticsearch。接下来的测试为方便直接采用 In-Memory 方式进行存储,生产推荐 Elasticsearch。
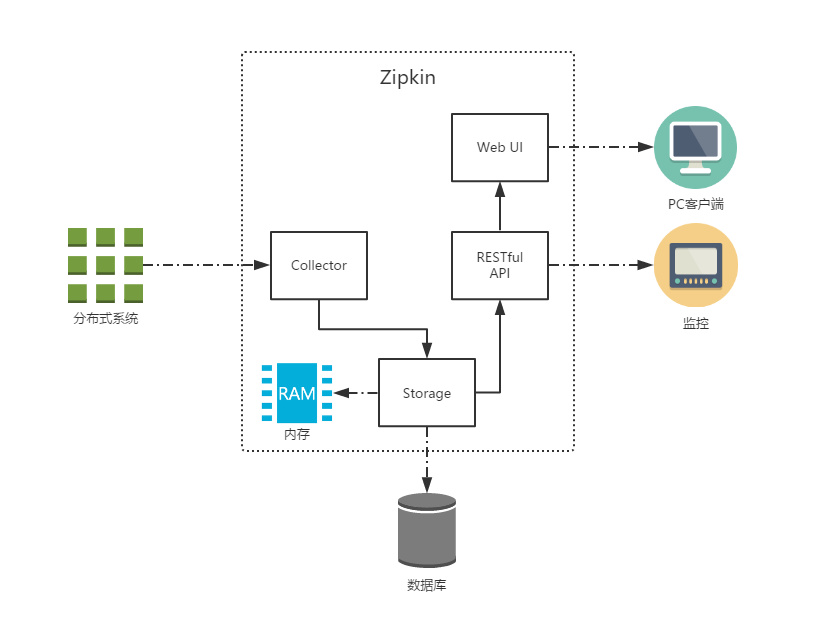
上图展示了 Zipkin 的基础架构,它主要由 4 个核心组件构成:
- Collector:收集器组件,它主要用于处理从外部系统发送过来的跟踪信息,将这些信息转换为 Zipkin 内部处理的 Span 格式,以支持后续的存储、分析、展示等功能。
- Storage:存储组件,它主要对处理收集器接收到的跟踪信息,默认会将这些信息存储在内存中,我们也可以修改此存储策略,通过使用其他存储组件将跟踪信息存储到数据库中。
- RESTful API:API 组件,它主要用来提供外部访问接口。比如给客户端展示跟踪信息,或是外接系统访问以实现监控等。
- Web UI:UI 组件,基于 API 组件实现的上层应用。通过 UI 组件用户可以方便而有直观地查询和分析跟踪信息。
快速上手
Zipkin 分为两端,一个是 Zipkin 服务端,一个是 Zipkin 客户端,客户端也就是微服务的应用。
客户端会配置服务端的 URL 地址,一旦发生服务间的调用的时候,会被配置在微服务里面的 Sleuth 的监听器监听,并生成相应的 Trace 和 Span 信息发送给服务端。
发送的方式主要有两种,一种是 HTTP 报文的方式,还有一种是消息总线的方式如 RabbitMQ。
不论哪种方式,我们都需要:
- 一个 Eureka 服务注册中心,这里我们就用之前的
eureka项目来当注册中心。 - 一个 Zipkin 服务端。
- 两个微服务应用,
trace-a和trace-b,其中trace-a中有一个 REST 接口/trace-a,调用该接口后将触发对trace-b应用的调用。
方式一:HTTP
在 Spring Cloud Sleuth 中对 Zipkin 的整合进行了自动化配置的封装,所以我们可以很轻松的引入和使用它。
Zipkin 服务端
关于 Zipkin 的服务端,在使用 Spring Boot 2.x 版本后,官方就不推荐自行定制编译了,反而是直接提供了编译好的 jar 包来给我们使用,详情请看 upgrade to Spring Boot 2.0 NoClassDefFoundError UndertowEmbeddedServletContainerFactory · Issue #1962 · openzipkin/zipkin · GitHub
并且以前的@EnableZipkinServer也已经被打上了@Deprecated
If you decide to make a custom server, you accept responsibility for troubleshooting your build or configuration problems, even if such problems are a reaction to a change made by the OpenZipkin maintainers. In other words, custom servers are possible, but not supported.
简而言之就是:私自改包,后果自负。
所以官方提供了一键脚本
1 | |
如果用 Docker 的话,直接
1 | |
任一方式启动后,访问 http://localhost:9411/zipkin/ 就能看到如下界面,嗯还有汉化看起来不错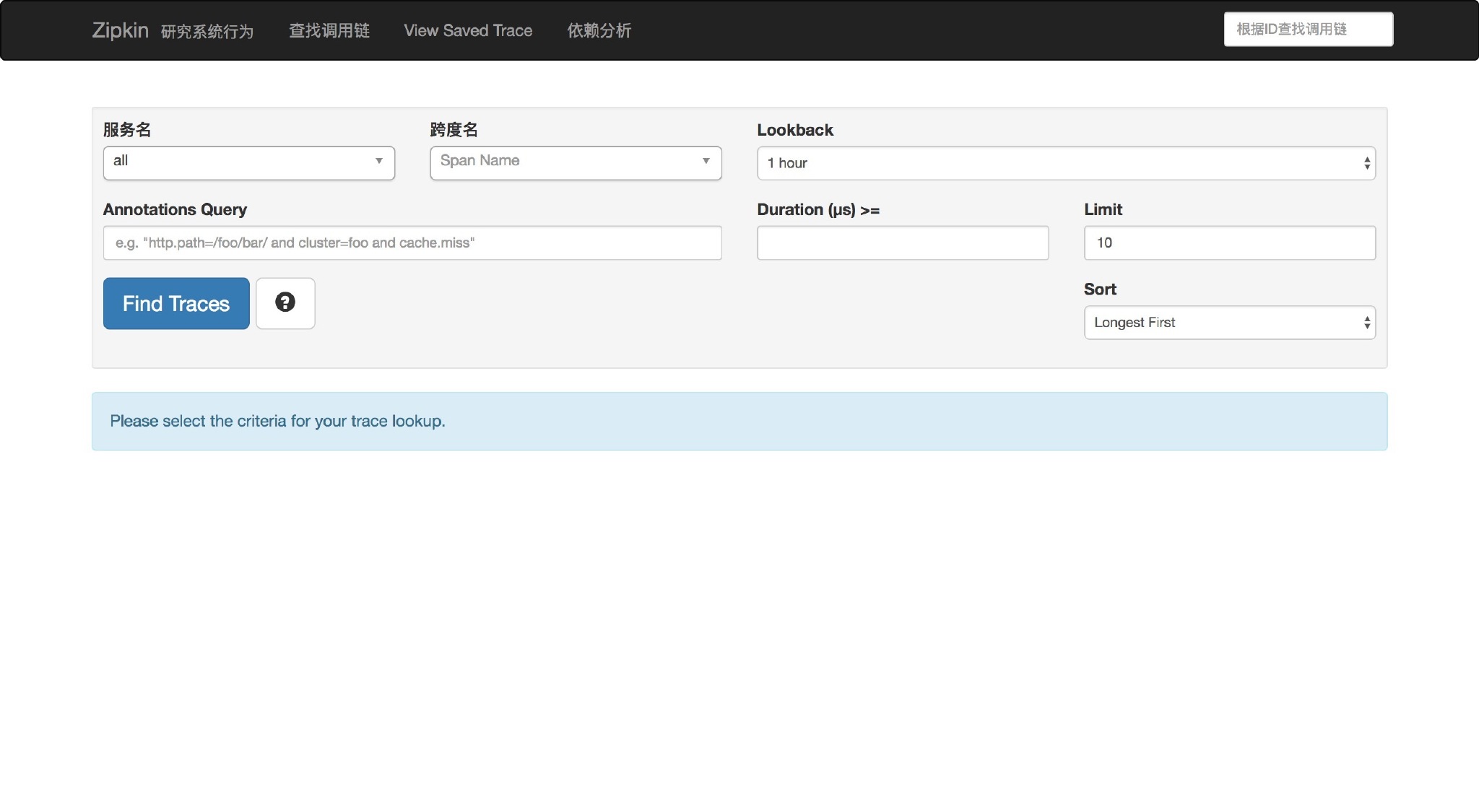
至此服务端就 OK 了。
微服务应用
创建两个基本的 Spring Boot 工程,名字分别为trace-a和trace-b。
两个工程的 pom.xml 均引入以下依赖坐标
1 | |
两者的配置文件也一样(除了spring. application.name和server.port,自行修改)
1 | |
Spring Cloud Sleuth 有一个 Sampler 策略,可以通过这个实现类来控制采样算法。采样器不会阻碍 span 相关 id 的产生,但是会对导出以及附加事件标签的相关操作造成影响。 Sleuth 默认采样算法的实现是 Reservoir sampling,具体的实现类是 PercentageBasedSampler,默认的采样比例为: 0.1(即 10%)。不过我们可以通过
spring.sleuth.sampler.percentage来设置,所设置的值介于 0.0 到 1.0 之间,1.0 则表示全部采集。
trace-a工程的启动类如下
1 | |
trace-b工程的启动类如下
1 | |
至此,一切就绪。Spring 应用在监测到 classpath 中有 Sleuth 和 Zipkin 后,会自动在 WebClient(或 RestTemplate)的调用过程中向 HTTP 请求注入追踪信息,并向 Zipkin Server 发送这些信息。
进行验证
我们分别启动 eureka、zipkin、trace-b、trace-a,然后
访问 http://localhost:8080/trace-a 可以得到返回值Trace,同时还能在它们的控制台中分别获得下面的输出:
1 | |
访问 http://localhost:9411/zipkin
点击 Find Traces 会看到有一条记录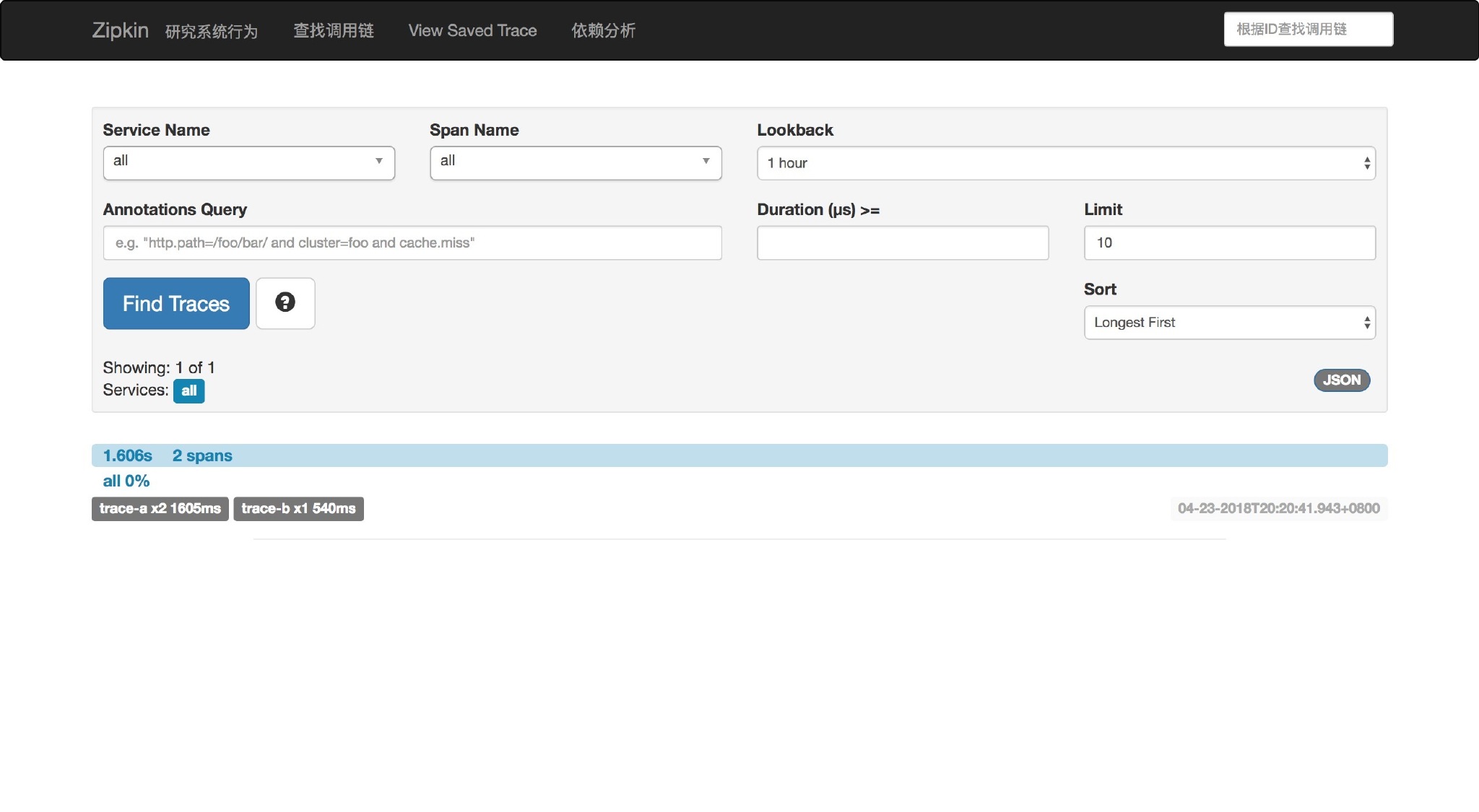
点击记录进去页面,可以看到每一个服务所耗费的时间和顺序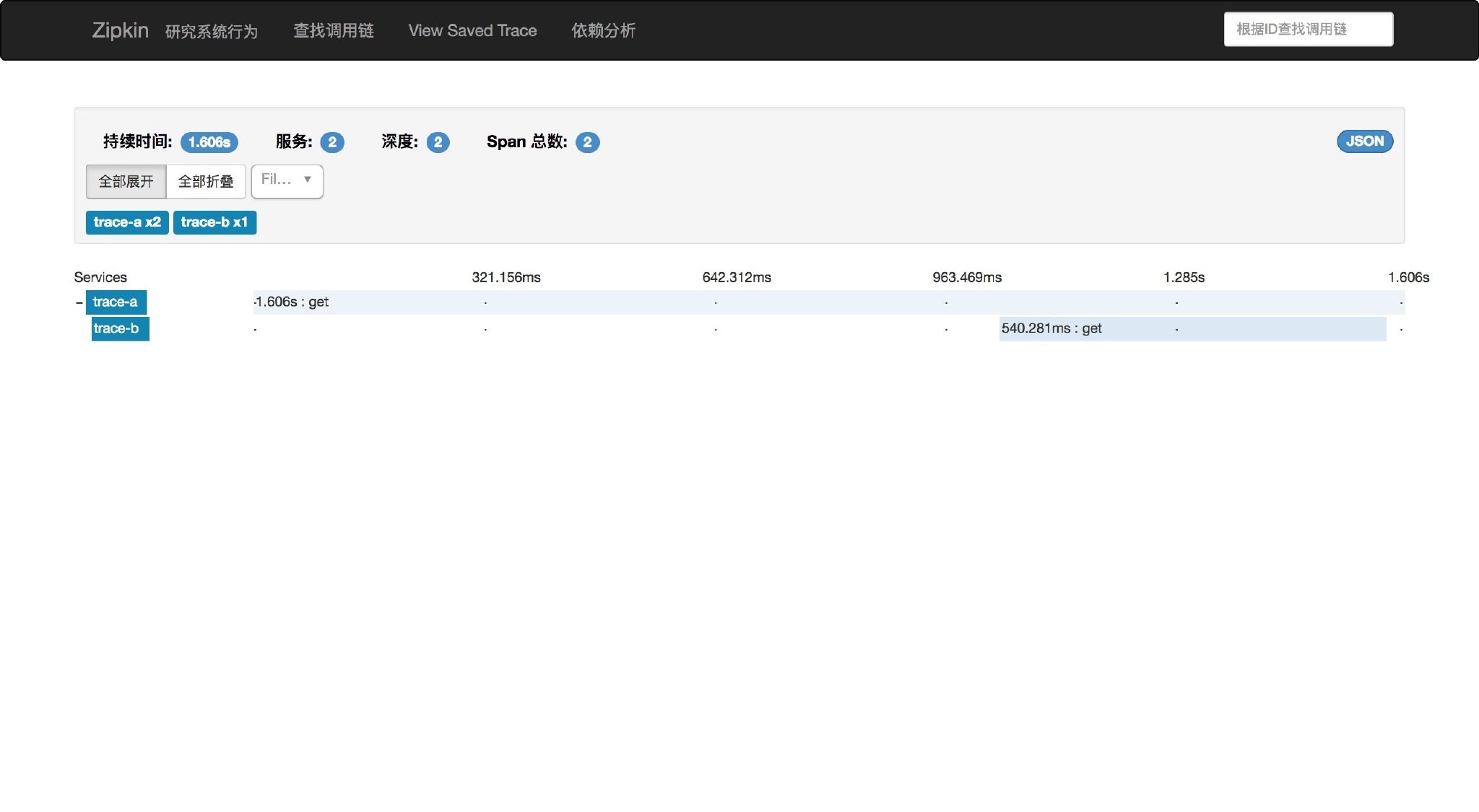
点击依赖分析,可以看到项目之间的调用关系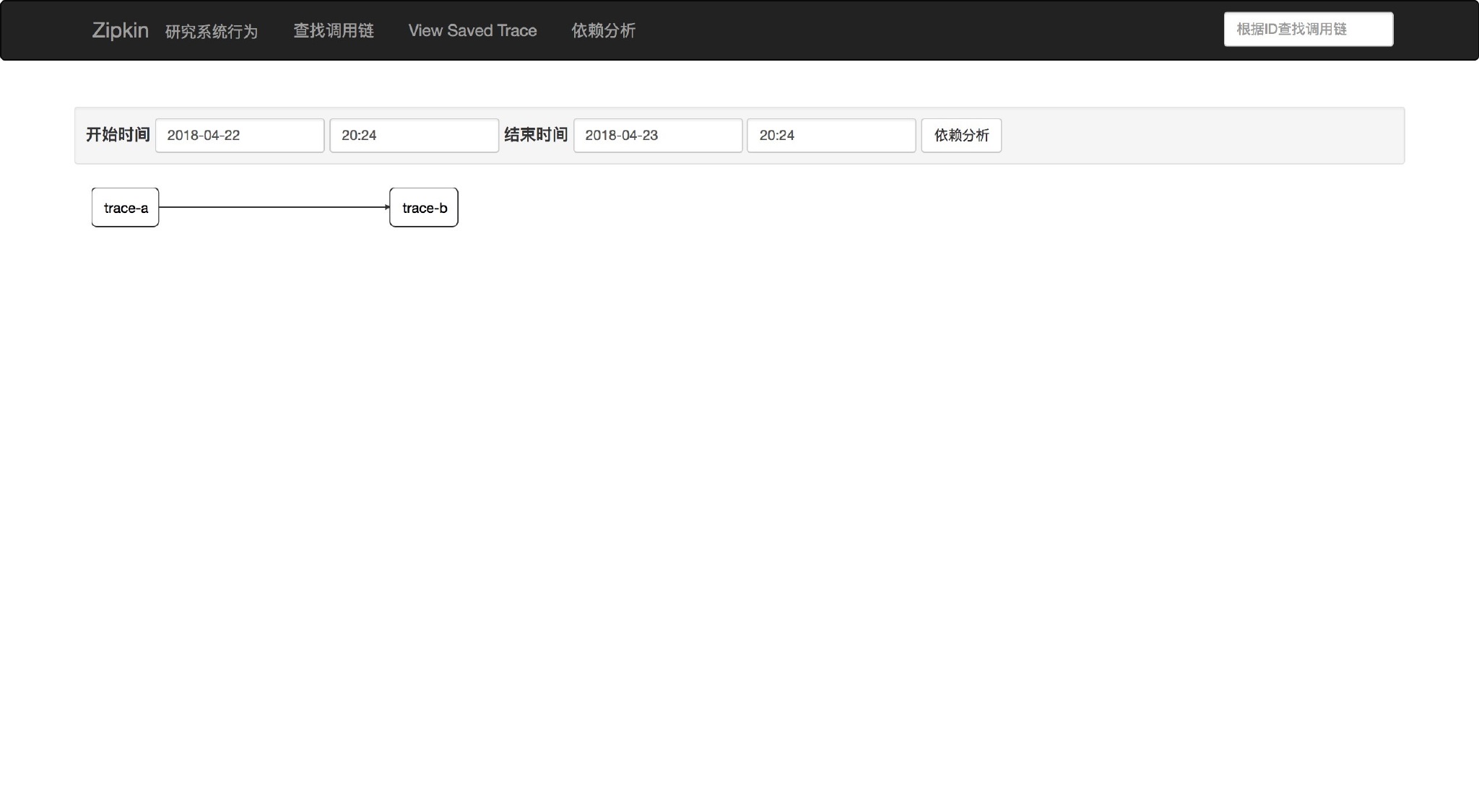
方式二:消息总线 RabbitMQ
因为之前说的 Zipkin 不再推荐我们来自定义 Server 端了,所以在最新版本的 Spring Cloud 依赖管理里已经找不到 zipkin-server 了。
那么如果直接用官方提供的 jar 包怎么从 RabbitMQ 中获取 trace 信息呢?
我们可以通过环境变量让 Zipkin 从 RabbitMQ 中读取信息,就像这样:
1 | |
可配置的环境变量如下表所示:
| 属性 | 环境变量 | 描述 |
|---|---|---|
zipkin.collector.rabbitmq.concurrency |
RABBIT_CONCURRENCY |
并发消费者数量,默认为1 |
zipkin.collector.rabbitmq.connection-timeout |
RABBIT_CONNECTION_TIMEOUT |
建立连接时的超时时间,默认为 60000毫秒,即 1 分钟 |
zipkin.collector.rabbitmq.queue |
RABBIT_QUEUE |
从中获取 span 信息的队列,默认为 zipkin |
zipkin.collector.rabbitmq.uri |
RABBIT_URI |
符合RabbitMQ URI 规范 的 URI,例如amqp://user:pass@host:10000/vhost |
如果设置了 URI,则以下属性将被忽略。
| 属性 | 环境变量 | 描述 |
|---|---|---|
zipkin.collector.rabbitmq.addresses |
RABBIT_ADDRESSES |
用逗号分隔的 RabbitMQ 地址列表,例如localhost:5672,localhost:5673 |
zipkin.collector.rabbitmq.password |
RABBIT_PASSWORD |
连接到 RabbitMQ 时使用的密码,默认为 guest |
zipkin.collector.rabbitmq.username |
RABBIT_USER |
连接到 RabbitMQ 时使用的用户名,默认为guest |
zipkin.collector.rabbitmq.virtual-host |
RABBIT_VIRTUAL_HOST |
使用的 RabbitMQ virtual host,默认为 / |
zipkin.collector.rabbitmq.use-ssl |
RABBIT_USE_SSL |
设置为true则用 SSL 的方式与 RabbitMQ 建立链接 |
关于 Zipkin 的 Client 端,也就是微服务应用,我们就在之前 trace-a、trace-b 的基础上修改,只要在他们的依赖里都引入spring-cloud-stream-binder-rabbit就好了,别的不用改。
1 | |
不过为了说明是通过 RabbitMQ 传输的信息,我将spring.zipkin.base-url均改为http://localhost:9412/,即指向一个错误的地址。
分别重启 trace-a、trace-b 工程,并启动 Zipkin Server
1 | |
然后访问 http://localhost:8080/trace-a 并刷新 Zipkin UI,看到如下内容,就说明 Sleuth+Zipkin+RabbitMQ 整合成功了。
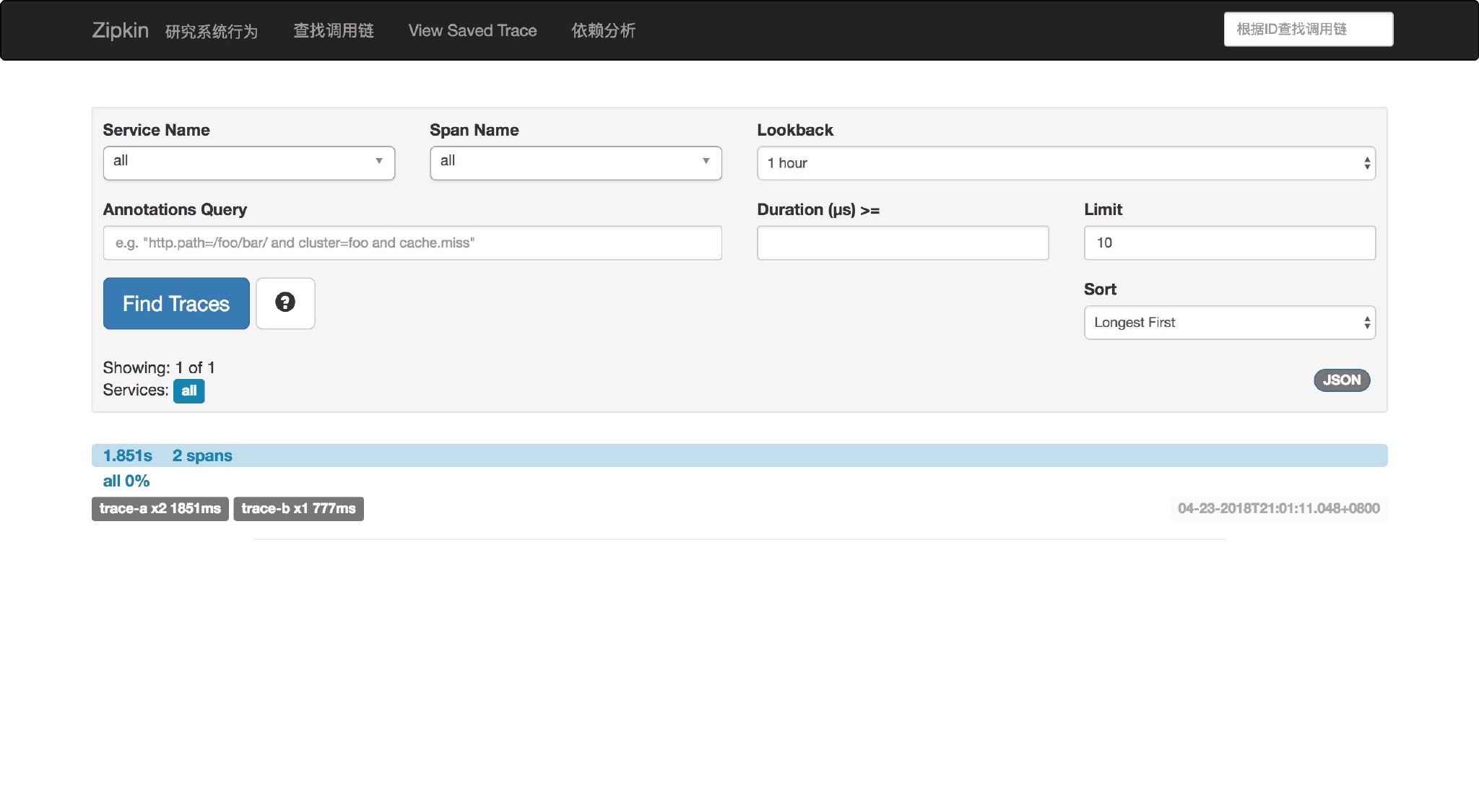
此时看 RabbitMQ Admin,会看到多了一个名为 zipkin 的 Queue
相关阅读
Spring Cloud(一):服务治理技术概览
Spring Cloud(二):服务注册与发现 Eureka
Spring Cloud(三):服务提供与调用 Eureka
Spring Cloud(四):服务容错保护 Hystrix
Spring Cloud(五):Hystrix 监控面板
Spring Cloud(六):Hystrix 监控数据聚合 Turbine
Spring Cloud(七):配置中心(Git 版与动态刷新)
Spring Cloud(八):配置中心(服务化与高可用)
Spring Cloud(九):配置中心(消息总线)
Spring Cloud(十):服务网关 Zuul(路由)
Spring Cloud(十一):服务网关 Zuul(过滤器)
Spring Cloud(十二):分布式链路跟踪(Sleuth 与 Zipkin)
示例代码:GitHub
参考
第六章:Spring Cloud Sleuth · SpringCloudTranslation
Spring Cloud Sleuth 进阶实战
Zipkin 分布式任务追踪
利用 Zipkin 对 Spring Cloud 应用进行服务追踪分析
Spring Cloud 技术分析(3)- spring cloud sleuth
upgrade to Spring Boot 2.0 NoClassDefFoundError UndertowEmbeddedServletContainerFactory
Spring Cloud Sleuth 2.0 Migration Guide
zipkin/zipkin-server at master
zipkin/zipkin-collector/rabbitmq at master